 |
Indotco InternationalIt's a personal service. |
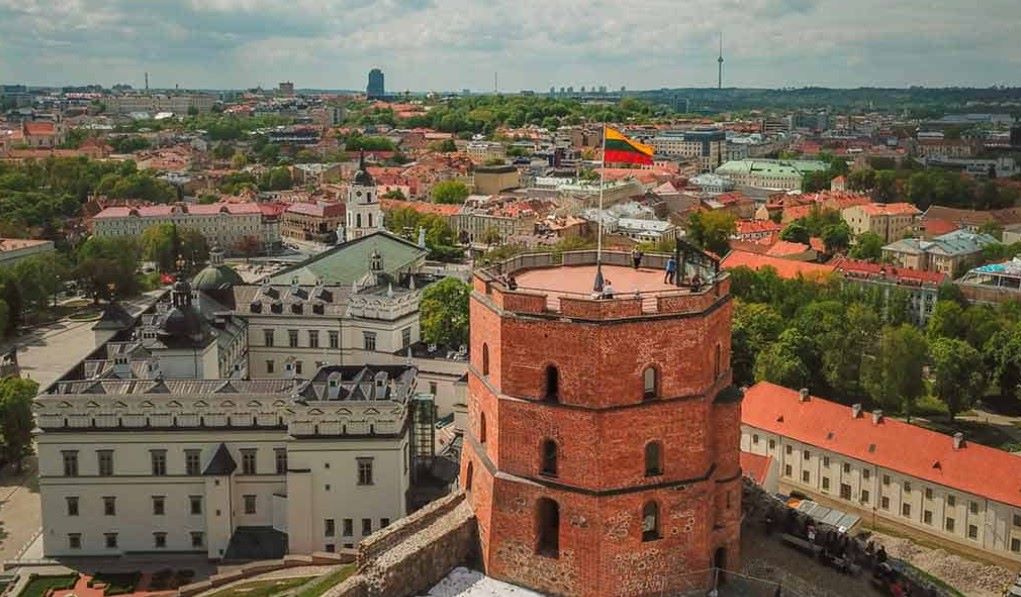

About Lithuania - History, Culture and Economy
Lithuania is a country with a rich history, vibrant culture, dynamic political landscape, and evolving economy. Here's an overview of each aspect:
History Ancient and Medieval Periods: - Early Inhabitants: The area now known as Lithuania has been inhabited for thousands of years, with evidence of human activity dating back to the Paleolithic period. - Grand Duchy of Lithuania: Established in the 13th century, it became one of the largest and most influential states in Europe. Under the leadership of Grand Duke Gediminas and later rulers, the Grand Duchy expanded its territories significantly. - Union with Poland: In 1386, Grand Duke Jogaila converted to Christianity and married the Polish queen, Jadwiga, creating a union between Lithuania and Poland. This led to the formation of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1569, a powerful and influential state until its partitions in the late 18th century. Modern Period: - Russian Empire: After the partitions of the Commonwealth, Lithuania was incorporated into the Russian Empire. - Independence: Lithuania declared independence on February 16, 1918, following World War I. However, it was occupied by Soviet and Nazi forces during World War II. - Soviet Era: Post-World War II, Lithuania was forcibly incorporated into the Soviet Union in 1944. It remained under Soviet control until the late 20th century. - Restoration of Independence: On March 11, 1990, Lithuania became the first Soviet republic to declare independence, leading to the reestablishment of a sovereign Lithuanian state. Culture Language: Lithuanian is one of the oldest languages in the world and one of the two surviving Baltic languages (the other being Latvian). It has preserved many archaic features no longer found in other Indo-European languages. Religion: The majority of Lithuanians are Roman Catholics, which plays a significant role in the country's cultural traditions and festivals. Arts and Literature: - Traditional Arts: Folk music, dances, and crafts are integral parts of Lithuanian culture. The "sutartinės," traditional multipart songs, are particularly unique. - Literature: Lithuania has a rich literary heritage with notable figures such as Kristijonas Donelaitis, who wrote "The Seasons," one of the first Lithuanian literary works. - Modern Culture: Contemporary Lithuanian culture is vibrant with numerous festivals, theaters, and a growing film industry. Politics Government Structure: Lithuania is a parliamentary democracy. The President is the head of state, elected for a five-year term. The Prime Minister, appointed by the President, is the head of government. The Seimas (Parliament) is a unicameral legislative body. Political Landscape: - Major Parties: Major political parties include the Homeland Union (conservative), the Lithuanian Social Democratic Party, and the Liberal Movement. - EU and NATO: Lithuania is a member of both the European Union and NATO, having joined both in 2004. These memberships significantly influence its foreign and domestic policies. Economy Overview: Lithuania has a mixed economy with a high-income status. It has undergone significant economic transformations since gaining independence from the Soviet Union, transitioning from a centrally planned economy to a market-based economy. Key Sectors: - Manufacturing: Includes production of machinery, electronics, and chemicals. - Services: The largest sector, including information technology, financial services, and tourism. - Agriculture: Important products include grain, potatoes, vegetables, and dairy products. Economic Challenges and Developments: - Growth: Lithuania has experienced robust economic growth, particularly after joining the EU, benefiting from access to the single market and structural funds. - Innovation and Technology: The country is focusing on innovation and technology, with a growing startup ecosystem and investments in high-tech industries. - Economic Challenges: Lithuania faces challenges such as demographic decline, emigration, and the need for further economic diversification. Lithuania’s journey from ancient times to the modern era reflects a nation resilient in preserving its identity, culture, and independence. Today, it stands as a dynamic member of the European community, continually evolving and adapting to new global realities. You have some more questions? Contact us for a free quote. |